Frontend implementation
Implementing OAuth 2.0 in the PERCEIVE Portal: A Frontend Guide
This guide outlines the steps and best practices for implementing OAuth 2.0 in the PERCEIVE Portal, a React-based web application. Utilizing the Authorization Code Flow with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) and refresh tokens, we aim to secure the application by integrating with our authorization server. This guide assumes familiarity with OAuth 2.0 concepts, for which you can refer to the detailed tokens article.
Overview of OAuth 2.0 Flow
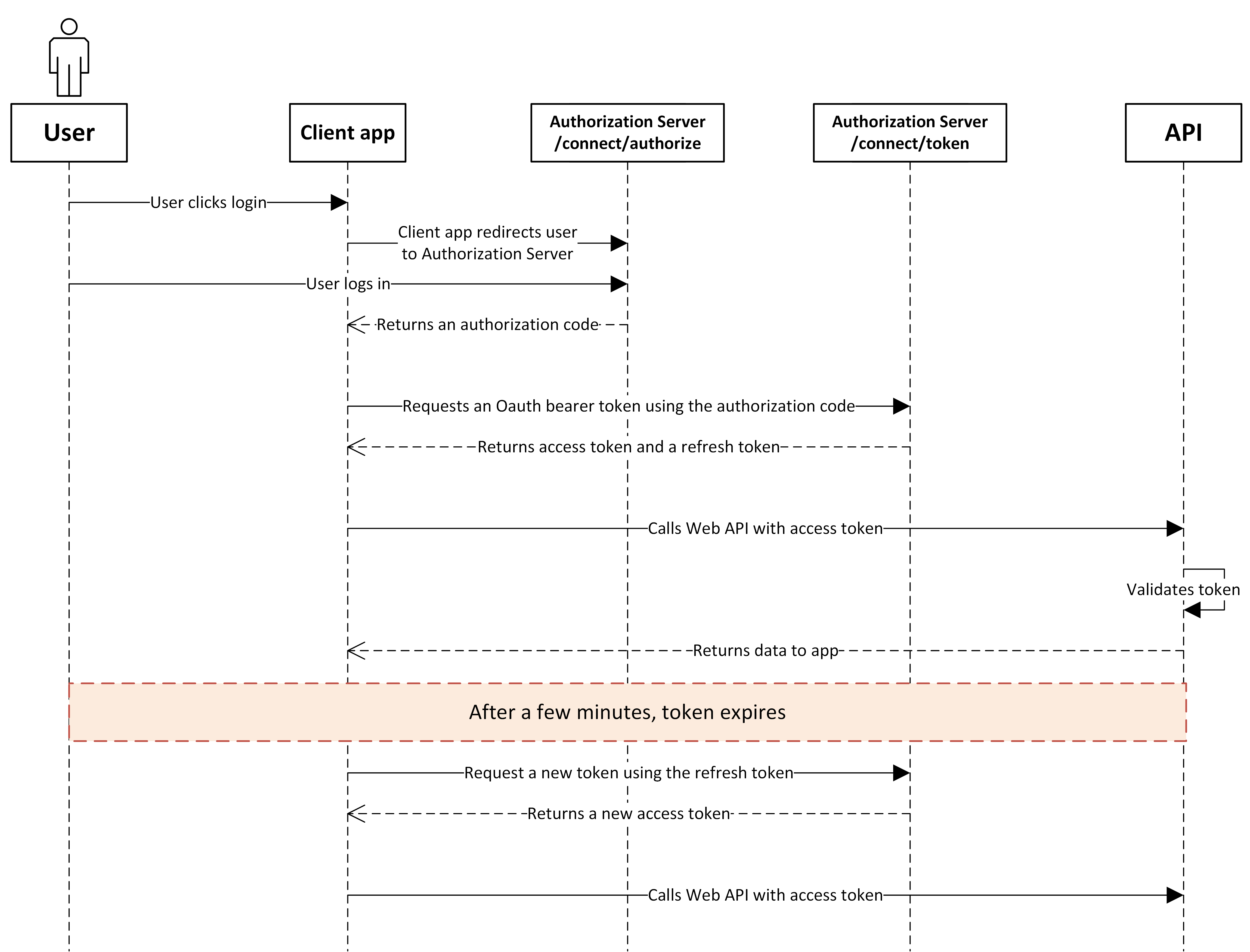
User Authentication and Authorization Code Retrieval:
The process begins with redirecting the user to the
/connect/authorizeendpoint of the authorization server to log in.Upon successful authentication, the authorization server redirects back to the application with an authorization code.
Exchange Authorization Code for Access Token:
The application exchanges the authorization code for an access and refresh token at the
/connect/tokenendpoint.
Using Access Tokens:
Access tokens (JWT) are used for making authenticated requests to resource servers.
Tokens should be stored securely and transmitted only over HTTPS.
Refreshing Access Tokens:
When the access token expires, use the refresh token to obtain a new access token and refresh token from the
/connect/tokenendpoint.
Logout:
To log out, redirect the user to the
/connect/logoutendpoint, ensuring the user is securely logged out from the application.
Step-by-Step Implementation
Step 1: Setting Up the Authorization Request
As recommended by the OAuth Security best practices, the authorization request requires PKCE.
Create a PKCE Code Verifier and Challenge:
Generate a secure, random string of between 43 and 128 characters. This string can consist of letters, digits, and the characters "-" (dash), "." (period), "_" (underscore), and "~" (tilde). e.g.
MfKQ9r8Gf4zYJLHW8nfw5h3xqTlNopApply the SHA-256 hashing algorithm to the string of characters.
Encode the hash using base64 URL encoding resulting in a string like
E3Zax5cVoV03zX9P5E5_L7-_Q2p3Z6E5hW5QvEpr2QM.
Redirect to the Authorization Endpoint:
Construct a URL to /connect/authorize with the following query parameters:
response_type=codeto specify the Authorization Code Flow.client_idwith your application's unique identifier. Please refer Clients and scopes for a complete list of clients.redirect_uriwhere the server will send the user after authorization.code_challengegenerated in the previous step.code_challenge_methodset toS256.statea unique and random string to prevent CSRF attacks.scopespecifying the access your application requests. Please refer to Clients and scopes for a complete list of scopes
Handling the Authorization Response
Capture the authorization code and state from the query parameters of the redirect URI.
Verify the returned state matches the one you sent in the authorization request to ensure the request's integrity.
Step 2: Exchanging the Authorization Code for Tokens
Making the Token Request:
Send a POST request to
/connect/tokenwith the following parameters in the request body:grant_type=authorization_codeto specify the type of operation.codethe authorization code received.redirect_urimust match the one used in the authorization request.client_idyour application's identifier.code_verifierthe original code verifier used to generate the challenge.
Handling the Token Response:
The response will include an
access_token(JWT),refresh_token, andexpires_indetailing the token's lifespan.Store these tokens securely and use the access token for authenticated requests to your API.
Step 3: Using Refresh Tokens
When the access token expires, use the refresh_token to obtain a new access token without requiring the user to log in again.
Make a POST request to
/connect/tokenwith:grant_type=refresh_tokenrefresh_tokenthe token you received alongside the access token.client_idyour application's identifier.
Step 4: Implementing Logout
To log out, redirect the user to the
/connect/logoutendpoint, optionally specifying apost_logout_redirect_urito navigate the user after logout.
Security Best Practices
Please refer to the security section in the Tokens article for secure token storage.
Please refer to the Security Considerations article for general OAuth security considerations.